You are viewing documentation for Flux version: 2.0
Version 2.0 of the documentation is no longer actively maintained. The site that you are currently viewing is an archived snapshot. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Blue/Green Deployments
This guide shows you how to automate Blue/Green deployments with Flagger and Kubernetes.
For applications that are not deployed on a service mesh, Flagger can orchestrate Blue/Green style deployments with Kubernetes L4 networking. When using a service mesh blue/green can be used as specified here.
Prerequisites
Flagger requires a Kubernetes cluster v1.16 or newer.
Install Flagger and the Prometheus add-on:
helm repo add flagger https://flagger.app
helm upgrade -i flagger flagger/flagger \
--namespace flagger \
--set prometheus.install=true \
--set meshProvider=kubernetes
If you already have a Prometheus instance running in your cluster, you can point Flagger to the ClusterIP service with:
helm upgrade -i flagger flagger/flagger \
--namespace flagger \
--set metricsServer=http://prometheus.monitoring:9090
Optionally you can enable Slack notifications:
helm upgrade -i flagger flagger/flagger \
--reuse-values \
--namespace flagger \
--set slack.url=https://hooks.slack.com/services/YOUR/SLACK/WEBHOOK \
--set slack.channel=some-channel-name \
--set slack.user=flagger
Bootstrap
Flagger takes a Kubernetes deployment and optionally a horizontal pod autoscaler (HPA), then creates a series of objects (Kubernetes deployment and ClusterIP services). These objects expose the application inside the cluster and drive the canary analysis and Blue/Green promotion.
Create a test namespace:
kubectl create ns test
Create a deployment and a horizontal pod autoscaler:
kubectl apply -k https://github.com/fluxcd/flagger//kustomize/podinfo?ref=main
Deploy the load testing service to generate traffic during the analysis:
kubectl apply -k https://github.com/fluxcd/flagger//kustomize/tester?ref=main
Create a canary custom resource:
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: Canary
metadata:
name: podinfo
namespace: test
spec:
# service mesh provider can be: kubernetes, istio, appmesh, nginx, gloo
provider: kubernetes
# deployment reference
targetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: podinfo
# the maximum time in seconds for the canary deployment
# to make progress before rollback (default 600s)
progressDeadlineSeconds: 60
# HPA reference (optional)
autoscalerRef:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
name: podinfo
service:
port: 9898
portDiscovery: true
analysis:
# schedule interval (default 60s)
interval: 30s
# max number of failed checks before rollback
threshold: 2
# number of checks to run before rollback
iterations: 10
# Prometheus checks based on
# http_request_duration_seconds histogram
metrics:
- name: request-success-rate
# minimum req success rate (non 5xx responses)
# percentage (0-100)
thresholdRange:
min: 99
interval: 1m
- name: request-duration
# maximum req duration P99
# milliseconds
thresholdRange:
max: 500
interval: 30s
# acceptance/load testing hooks
webhooks:
- name: smoke-test
type: pre-rollout
url: http://flagger-loadtester.test/
timeout: 15s
metadata:
type: bash
cmd: "curl -sd 'anon' http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/token | grep token"
- name: load-test
url: http://flagger-loadtester.test/
timeout: 5s
metadata:
type: cmd
cmd: "hey -z 1m -q 10 -c 2 http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/"
The above configuration will run an analysis for five minutes.
Save the above resource as podinfo-canary.yaml and then apply it:
kubectl apply -f ./podinfo-canary.yaml
After a couple of seconds Flagger will create the canary objects:
# applied
deployment.apps/podinfo
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/podinfo
canary.flagger.app/podinfo
# generated
deployment.apps/podinfo-primary
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/podinfo-primary
service/podinfo
service/podinfo-canary
service/podinfo-primary
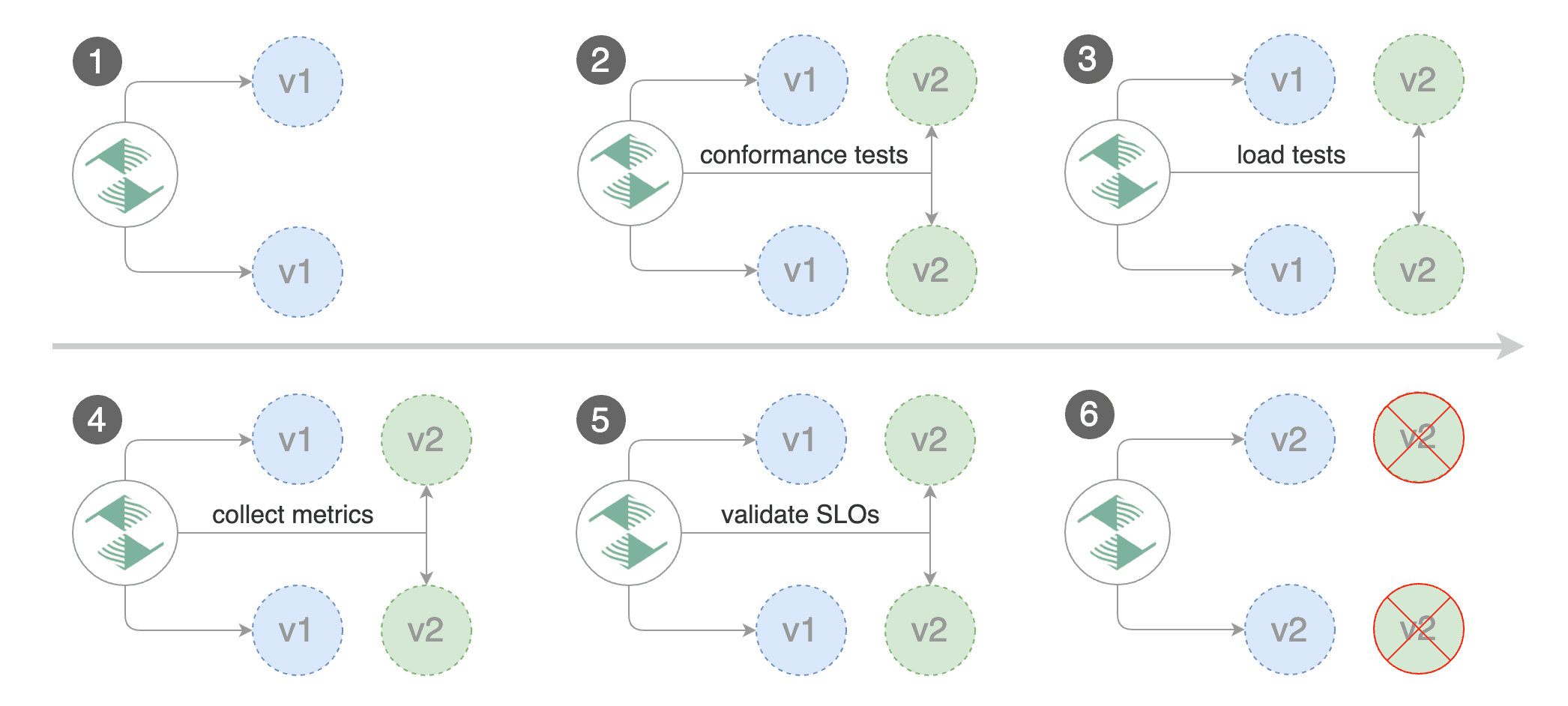
Blue/Green scenario:
on bootstrap, Flagger will create three ClusterIP services (
app-primary,app-canary,app)and a shadow deployment named
app-primarythat represents the blue versionwhen a new version is detected, Flagger would scale up the green version and run the conformance tests
(the tests should target the
app-canaryClusterIP service to reach the green version)if the conformance tests are passing, Flagger would start the load tests and validate them with custom Prometheus queries
if the load test analysis is successful, Flagger will promote the new version to
app-primaryand scale down the green version
Automated Blue/Green promotion
Trigger a deployment by updating the container image:
kubectl -n test set image deployment/podinfo \
podinfod=ghcr.io/stefanprodan/podinfo:6.0.1
Flagger detects that the deployment revision changed and starts a new rollout:
kubectl -n test describe canary/podinfo
Events:
New revision detected podinfo.test
Waiting for podinfo.test rollout to finish: 0 of 1 updated replicas are available
Pre-rollout check acceptance-test passed
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 1/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 2/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 3/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 4/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 5/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 6/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 7/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 8/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 9/10
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 10/10
Copying podinfo.test template spec to podinfo-primary.test
Waiting for podinfo-primary.test rollout to finish: 1 of 2 updated replicas are available
Promotion completed! Scaling down podinfo.test
Note that if you apply new changes to the deployment during the canary analysis, Flagger will restart the analysis.
You can monitor all canaries with:
watch kubectl get canaries --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME STATUS WEIGHT LASTTRANSITIONTIME
test podinfo Progressing 100 2019-06-16T14:05:07Z
prod frontend Succeeded 0 2019-06-15T16:15:07Z
prod backend Failed 0 2019-06-14T17:05:07Z
Automated rollback
During the analysis you can generate HTTP 500 errors and high latency to test Flagger’s rollback.
Exec into the load tester pod with:
kubectl -n test exec -it flagger-loadtester-xx-xx sh
Generate HTTP 500 errors:
watch curl http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/status/500
Generate latency:
watch curl http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/delay/1
When the number of failed checks reaches the analysis threshold, the green version is scaled to zero and the rollout is marked as failed.
kubectl -n test describe canary/podinfo
Status:
Failed Checks: 2
Phase: Failed
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Synced 3m flagger New revision detected podinfo.test
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 1/10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 2/10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 3/10
Normal Synced 3m flagger Halt podinfo.test advancement success rate 69.17% < 99%
Normal Synced 2m flagger Halt podinfo.test advancement success rate 61.39% < 99%
Warning Synced 2m flagger Rolling back podinfo.test failed checks threshold reached 2
Warning Synced 1m flagger Canary failed! Scaling down podinfo.test
Custom metrics
The analysis can be extended with Prometheus queries. The demo app is instrumented with Prometheus so you can create a custom check that will use the HTTP request duration histogram to validate the canary (green version).
Create a metric template and apply it on the cluster:
apiVersion: flagger.app/v1beta1
kind: MetricTemplate
metadata:
name: not-found-percentage
namespace: test
spec:
provider:
type: prometheus
address: http://flagger-prometheus.flagger:9090
query: |
100 - sum(
rate(
http_request_duration_seconds_count{
kubernetes_namespace="{{ namespace }}",
kubernetes_pod_name=~"{{ target }}-[0-9a-zA-Z]+(-[0-9a-zA-Z]+)"
status!="{{ interval }}"
}[1m]
)
)
/
sum(
rate(
http_request_duration_seconds_count{
kubernetes_namespace="{{ namespace }}",
kubernetes_pod_name=~"{{ target }}-[0-9a-zA-Z]+(-[0-9a-zA-Z]+)"
}[{{ interval }}]
)
) * 100
Edit the canary analysis and add the following metric:
analysis:
metrics:
- name: "404s percentage"
templateRef:
name: not-found-percentage
thresholdRange:
max: 5
interval: 1m
The above configuration validates the canary (green version) by checking if the HTTP 404 req/sec percentage is below 5 percent of the total traffic. If the 404s rate reaches the 5% threshold, then the rollout is rolled back.
Trigger a deployment by updating the container image:
kubectl -n test set image deployment/podinfo \
podinfod=ghcr.io/stefanprodan/podinfo:6.0.3
Generate 404s:
watch curl http://podinfo-canary.test:9898/status/400
Watch Flagger logs:
kubectl -n flagger logs deployment/flagger -f | jq .msg
New revision detected podinfo.test
Scaling up podinfo.test
Advance podinfo.test canary iteration 1/10
Halt podinfo.test advancement 404s percentage 6.20 > 5
Halt podinfo.test advancement 404s percentage 6.45 > 5
Rolling back podinfo.test failed checks threshold reached 2
Canary failed! Scaling down podinfo.test
If you have alerting configured, Flagger will send a notification with the reason why the canary failed.
Conformance Testing with Helm
Flagger comes with a testing service that can run Helm tests when configured as a pre-rollout webhook.
Deploy the Helm test runner in the kube-system namespace using the tiller service account:
helm repo add flagger https://flagger.app
helm upgrade -i flagger-helmtester flagger/loadtester \
--namespace=kube-system \
--set serviceAccountName=tiller
When deployed the Helm tester API will be available at http://flagger-helmtester.kube-system/.
Add a helm test pre-rollout hook to your chart:
analysis:
webhooks:
- name: "conformance testing"
type: pre-rollout
url: http://flagger-helmtester.kube-system/
timeout: 3m
metadata:
type: "helm"
cmd: "test {{ .Release.Name }} --cleanup"
When the canary analysis starts, Flagger will call the pre-rollout webhooks. If the helm test fails, Flagger will retry until the analysis threshold is reached and the canary is rolled back.
For an in-depth look at the analysis process read the usage docs.